Note
An epsilon () transition is a transition that the FA can make without consuming an input character.
We can translate NFAs to DFAs. IOW, whatever an NFA can do, a DFA can do.
Regex to DFA
Uses Syntax Directed Translation
- NFAs make it easy to capture disjunctive choice (regex → NFA)
- NFA → DFA
- Minimize and optimize DFA
DFA Minimization
- Merge all accepting states
- Merge all non-accepting states
- Add the error state
- Remove ambiguity (split ambiguous state into 2 states that are distinct)
- Repeat
Some Notation
- The NFA states are labelled with numbers
- The DFA states are labelled with letters
- The DFA have have exponentially more states than the NFA
Granular Examples
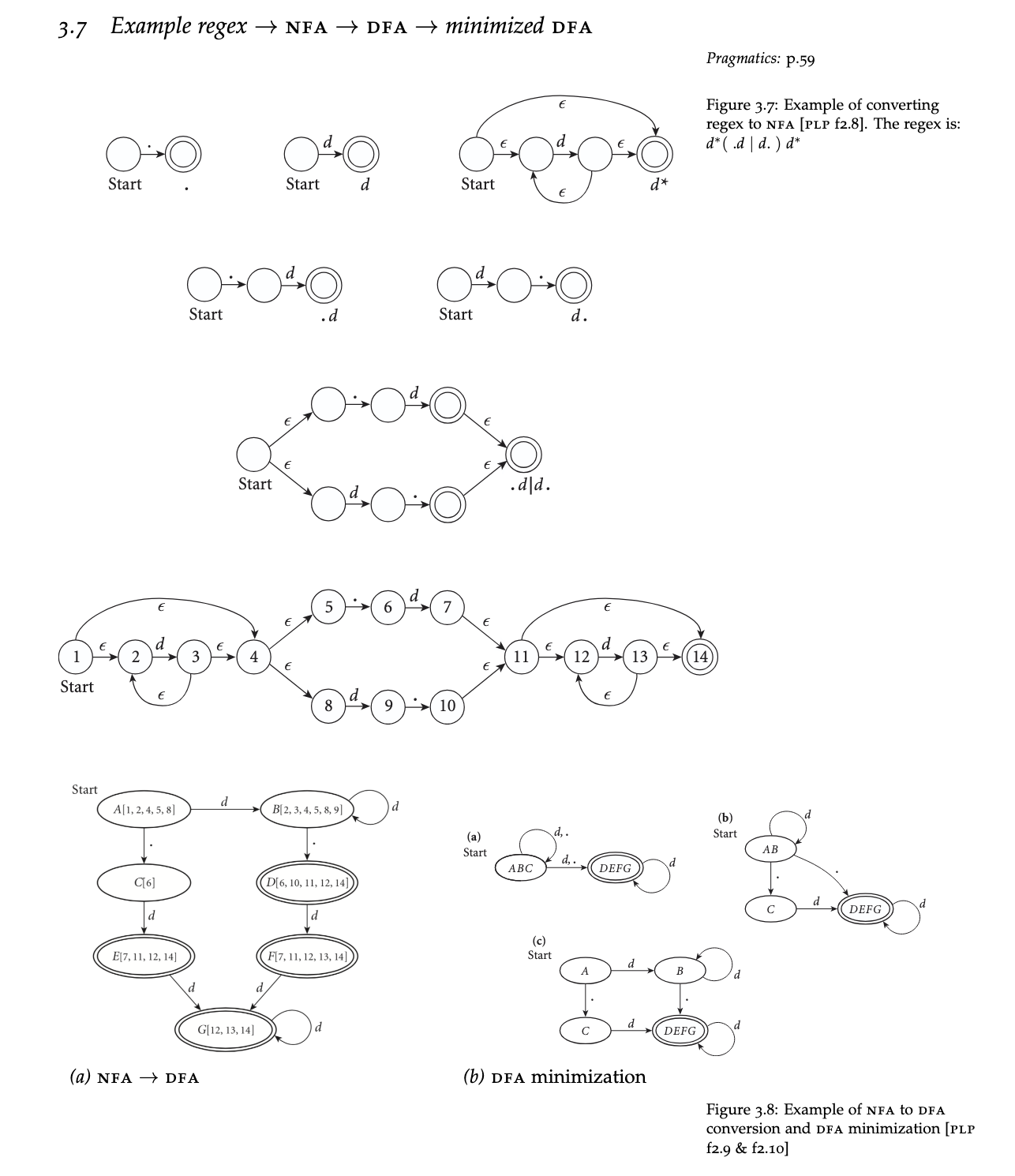
Regex → NFA
Operator transition rules:
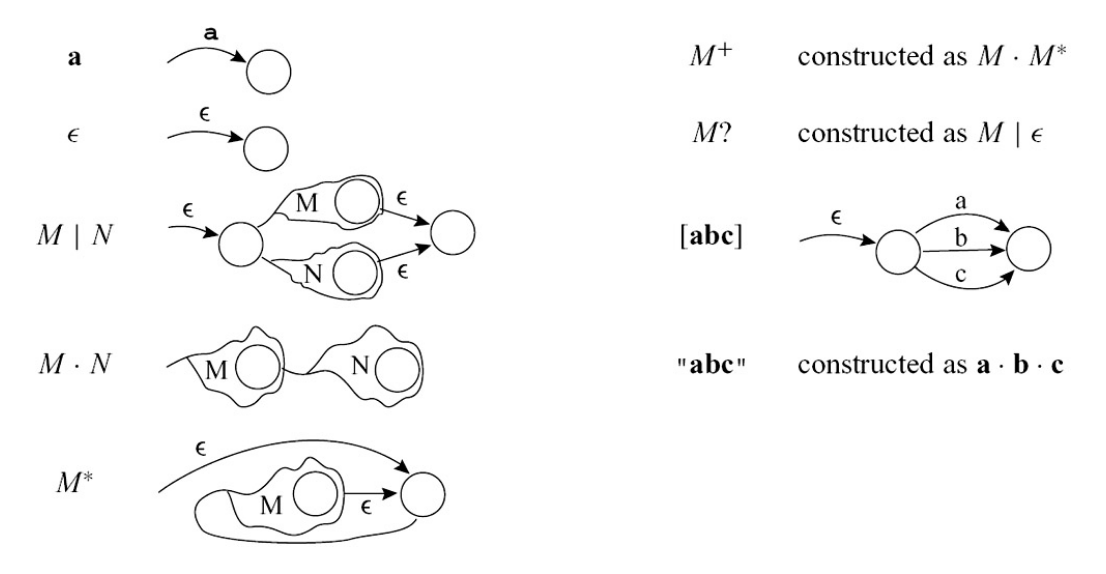
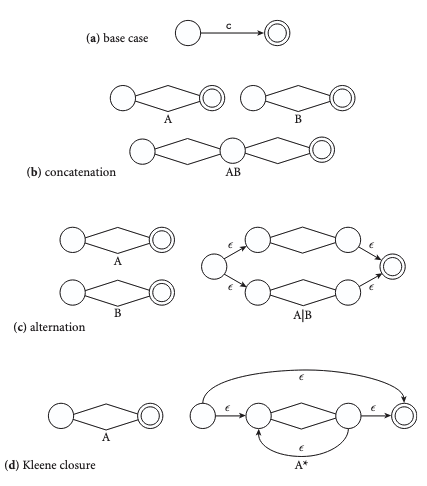
- The strategy…
- Given a regex (ex. )
- Identify the base pieces
- , ,
- Create sub-NFAs for these base pieces
- Connect the sub-NFAs with transitions using operator rules (where , concatenation, kleene star, etc have different transition rules which are shown above)
- Identify the base pieces
NFA → DFA
- Create initial DFA state A which is the NFA start state and all states reachable through
- For each letter , see which DFA states it transitions to from the DFA states included in A and the ones that those states can get to from
DFA Minimization
- Merge all final states into a new final state
- Merge all non-final states into a new non-final state
- This will not be legal at this point because it will have ambiguous transitions
- Iterate through all ambiguous transitions and split the start state such that there are no more ambiguous transitions
- Look for states that do the same thing and condense them into a single state
- Split states with ambiguity into two states
- Repeat until no ambiguity (DFA)
- E2E Example*